TeLEOS-2 will be able to provide all-weather day and night coverage, and capable of imaging at 1m full-polarimetric resolution.
POEM upper stage will host seven payloads / in-orbit experiments

The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO)'s PSLV-C55 mission will launch a dedicated commercial mission through NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) for an international satellite customers from Singapore with TeLEOS-2 as primary satellite and Lumelite-4 as a rideshare satellite.
Liftoff is scheduled for April 22, 2023 at 14:19 hours IST (0849 UTC) from the first launch pad in Sriharikota spaceport on India's east coast near Chennai.

This is the 57th flight of PSLV and 16th mission using the PSLV Core Alone configuration (PSLV-CA), The 228.3-ton rocket will take-off pointing to a launch azimuth of 104°, These payloads are intended to be launched and deployed into an Low Earth Orbit, with a low inclination of 10° at an altitude of 586 km.
Payloads
TeLEOS-2
The TeLEOS-2 satellite is developed under a partnership between DSTA (representing the Government of Singapore) and ST Engineering. Once deployed and operational, it will be used to support the satellite imagery requirements of various agencies within the Government of Singapore. TeLEOS-2 carries a Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) payload. TeLEOS-2 will be able to provide all-weather day and night coverage, and capable of imaging at 1m full-polarimetric resolution.

Singapore Technologies Electronics Limited (ST Electronics) currently known as ST Engineering has announced a new partnership with the Defence Science & Technology Agency (DSTA) to develop the next generation Earth Observation Satellite, TeLEOS-2. The announcement was made at the Global Space Technology Convention (GSTC) in 2017, where ST Engineering showcased its latest technological advancements.
Following the success of TeLEOS-1, which was Singapore's first made-in-Singapore commercial Earth Observation Satellite, the development of TeLEOS-2 is expected to further boost the growth of Singapore's space industry. With the support of DSTA, ST Engineering aims to strengthen its position in the global space market and expand its portfolio of space-related products and services.
TeLEOS-2 is expected to have advanced capabilities compared to its predecessor. The satellite will feature higher resolution imaging and enhanced data processing capabilities, which will allow for more accurate and detailed analysis of the earth's surface. This will have significant applications in various fields, including urban planning, agriculture, maritime surveillance, and disaster management.

The development of TeLEOS-2 is part of Singapore's broader strategy to build a robust space industry and increase its presence in the global space market. The country has made significant investments in research and development, as well as in the training of skilled professionals in the space industry. The development of TeLEOS-2 will also create new opportunities for local businesses and help to foster innovation in the industry.
Overall, the partnership between ST Engineering and DSTA to develop TeLEOS-2 is a significant milestone for Singapore's space industry. The satellite's advanced capabilities and the partnership's technological expertise are expected to further enhance Singapore's position as a key player in the global space market.
LUMILITE-4
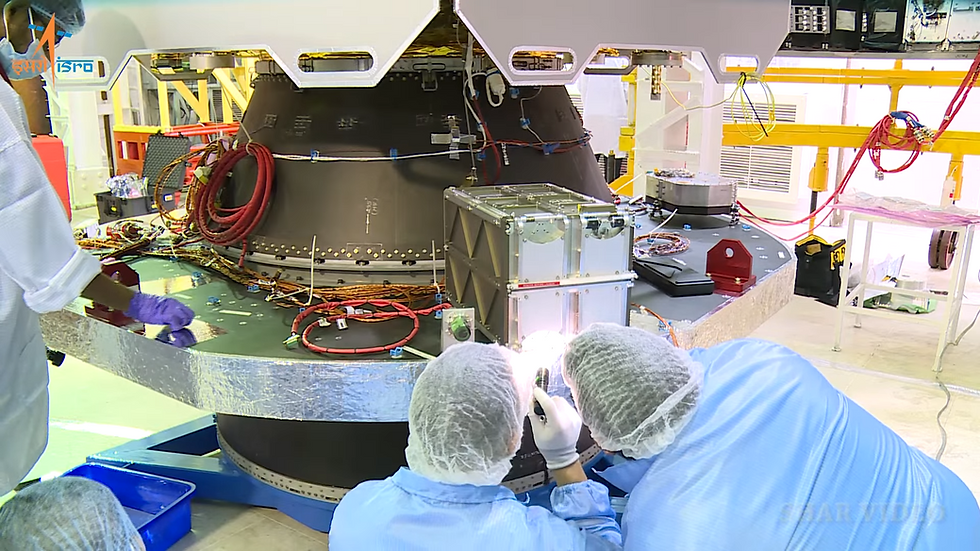
The LUMELITE-4 satellite is co-developed by the Institute for Infocomm Research (I2R) of A*STAR and Satellite Technology and Research Centre (STAR) of the National University of Singapore. LUMELITE4 is an advanced 12U satellite developed for the technological demonstration of the High-Performance Space-borne VHF Data Exchange System (VDES). Using the VDES communication payload developed by I2R and STAR’s scalable satellite bus platform, it aims to augment Singapore’s e-navigation maritime safety and benefit the global shipping community.

Presently, STAR is building concurrently 5 satellites. The flagship program is a formation flying of 3 satellites named Lumelite-1, -2 and -3. These 3 satellites will be flying with a separation distance between 50 and 200km. These satellites have inter-satellite communication capability, precise clock synchronization, and accurate relative ranging technology. Lumelite-4 is another program demonstrating VDES application for maritime safety and communication. Lumelite-1 to -4 are 12u CubeSat size (approximately 20x20x30cm). Lumelite-5 is a larger 50kg satellite with a dimension approximately 50x50x50cm. It is designed to demonstrate high data rate communication between a low earth orbit satellite and a medium earth orbit satellite.
PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-2 (POEM-2)

PSLV-C55 mission will carry out in-orbit scientific experiments by using the spent PS4 stage as an orbital platform. This is the third time that PS4 will be used after satellite separations as a platform for experiments. There will be non-separable payloads mounted on MSA. Payloads will be powered ON by a command, after all satellites are separated. The platform will have solar panel mounted around PS4 tank which will be deployed after confirmation of the stage
achieving stabilization. The deployment of the solar panels will be through a ground command. The platform will ensure that the deployed solar panel points towards the Sun optimally using appropriate sun pointing mode, which will increase the power generation capability of the platform. The power will be provided to payloads and avionic packages based on their requirements.
PSLV OEM-2 payloads:
PILOT
PILOT stands for PSLV In-Orbital OBC and Thermals is a 1U payload for the PS4 stage of PSLV-C55 (POEM-2) developed at SSPACE. I proposed the project during the last semester of my B.tech program at IIST. PILOT consists of an On-board computer, a PSLV interface board and a sensor board.

Brief specifications of PILOT are as follows -
Size - 1U (10 cm x 10 cm x 10 cm )
Mass < 1kg
Power - 5 V/ 2 W
The objectives of PILOT are as follows -
1. In-orbit qualification of On-board computer
This on-board computer is planned to support multiple future missions of IIST. PILOT would help to understand the behaviour of the OBC in the orbit. Especially focusing on the number of resets, SEU, SEL and the behaviour of a commercial SD-card.
2. Thermal Body Validation Various sensors are put on the PILOT’s body. Temperatures from all these sensors for thermal model validation of the structure.
3. Validation of in-house flight software PILOT’s OBC runs a flight software fully developed by students at IIST. This mission will help students getting a hands-on experience on developing software for small satellites.
ARIS-2 (Advanced Retarding potential analyser for Ionosphere Studies): A payload by IIST for ionosphere studies in LEO and it is linked to proposed MOM-2 and Venus missions. ARIS-1 flew on PSLV-C45/EMISAT in April 2019.
Starberry-Sense: A low-cost Raspberry Pi Zero based star sensor developed by Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) for cubesat application.
ARKA200: Xenon based Hall-effect thruster (HET) by Bellatrix with heaterless hollow cathode.

In 2021 Bellatrix tested India’s first privately built Hall Thruster — a highly efficient electric propulsion system for satellites — has since signed an agreement with L&T to enhance capacity. It was also the first to develop the world’s first commercial Microwave Plasma Thruster, which uses water as fuel, and for which the company had bagged an order from ISRO. A Hall Thruster, initially developed in Russia, is a device that employs electric and magnetic fields to ionise propellant gases such as Xenon to produce thrust. Today, it is the most reliable and time-tested electric propulsion system in the global market. And as per Bellatrix, this thruster also forms a critical technology for its Space taxi or OTV. The firm has collaborations with other space companies — SatSure, Skyroot Aerospace and Dhruva Space — on its ambitious orbital transfer vehicle (OTV) mission.
3U Satellite Orbital Deployer (DSOD-3U) & 6U Satellite Orbital Deployer (DSOD-6U)

Dhruva Space will be testing their 3U and 6U Satellite Orbital Deployers; these deployers are able to accommodate more or larger CubeSats.
The DSOD-3U is an extension of the DSOD-1U, the DSOD-6U will be tested for delayed deployment of satellites in LEO or higher orbits. This will essentially let customers leverage the Dhruva Space deployers for storing satellites in orbit or utilisation of the same for Lunar missions.
Dhruva Space Orbital Link (DSOL)
The company will also be testing its Dhruva Space Orbital Link (DSOL). The Orbital Link is designed and being tested to support satellite-based data relay applications.
DSOL Mission’s in-Space experiments by Dhruva Space will utilise the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module (POEM) which allows in-orbit scientific experiments using the spent PS4 stage as an orbital platform.
Ahead of the launch, Sanjay Nekkanti, CEO, Dhruva Space, comments, “Dhruva Space’s mission is to make building, launching and operations of satellites and satellite constellation mission as seamless as possible while not compromising on cost, reliability and turnaround times. We look forward to testing our larger classes of separation systems so that customers can leverage these deployers to launch their own payloads beyond Earth’s Orbit. Our Dhruva Space Orbital Link will also be integral in the larger nano (P-30) and micro (P-90) satellite platforms of Dhruva Space.”
Nekkanti continues, “The developing coordination between private and Government Space industries is flourishing. We would like to express our appreciation and gratitude towards the Department of Space, Government of India; the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO); NewSpace India Limited (NSIL); Indian National Space Promotion and Authorisation Centre (IN-SPACe); Vikram Sarabhai Space Centre (VSSC); and Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SDSC) for the guidance and encouragement to our team members. We would also like to thank our vendors, partners and peers who have all contributed to the upcoming missions in very important ways. We are also very excited about the announcement of the Indian Space Policy this week, and are eagerly looking forward to the FDI Policy and Space Act to come into effect in the near future.”
PSLV-C55 Flight Profile:








Comments